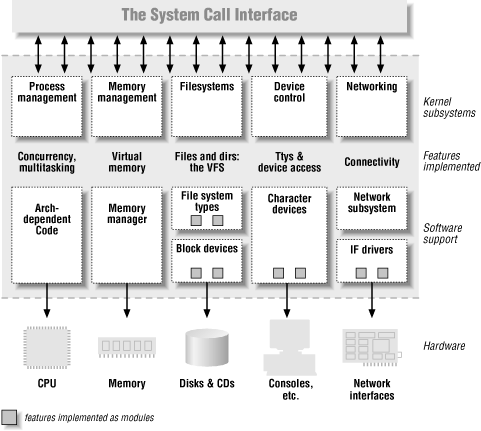
Character Device Driver
Device Driver Types
- Character-based device drivers
- Block-based device drivers
- Network device drivers
- USB and etc
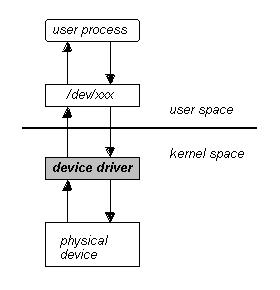
How to use device drivers from an application
- Device drivers are treated as files with specific file types
- Treated as a file, but target is an actual device
Example with ttyS0
- Application code
int fd_in, count;
char buf[1024];
fd_out = open(“/dev/ttyS0”, O_WRONLY);
strcpy(buf, "Hello\n");
write(fd_out, buf, strlen(buf));
........
-
Corresponding kernel part
-
sys_write()
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(write, unsigned int, fd, const char __user *, buf,
size_t, count)
{
struct file *file;
ssize_t ret = -EBADF;
int fput_needed;
file = fget_light(fd, &fput_needed);
if (file) {
loff_t pos = file_pos_read(file);
ret = vfs_write(file, buf, count, &pos);
file_pos_write(file, pos);
fput_light(file, fput_needed);
}
return ret;
}
- vfs_write() which is called from sys_write()
ssize_t vfs_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
ssize_t ret;
...
ret = rw_verify_area(WRITE, file, pos, count);
if (ret >= 0) {
count = ret;
if (file->f_op->write)
ret = file->f_op->write(file, buf, count, pos);
else
ret = do_sync_write(file, buf, count, pos);
...
}
return ret;
}
- Actual operation on 8250.c
static void
serial8250_console_write(struct console *co, const char *s, unsigned int count)
{
struct uart_8250_port *up = &serial8250_ports[co->kernel/internals/index];
unsigned long flags;
unsigned int ier;
int locked = 1;
touch_nmi_watchdog();
local_irq_save(flags);
if (up->port.sysrq) {
/* serial8250_handle_port() already took the lock */
locked = 0;
} else if (oops_in_progress) {
locked = spin_trylock(&up->port.lock);
} else
spin_lock(&up->port.lock);
...
What error codes can we return to applications
-
Error codes are defined in ‘include/asm-generic/errno-base.h’ and ‘include/asm-generic/errno.h’
-
Example)
-
Kernel code for 8250 setup
static int __init serial8250_console_setup(struct console *co, char *options)
{
...
if (!port->iobase && !port->membase)
return -ENODEV;
...
- Application code to check above
int main( int argc, char **argv )
{
int fd_out = 0;
fd_out = open(“/dev/ttyS0”, O_WRONLY);
if( fd_out < 0 ) {
perror( "Error opening file" );
printf( "Error opening file: %s\n", strerror( errno ) );
}
...
How to leave logs for errors
- All logs are generated via ‘printk()’ function
asmlinkage int printk(const char * fmt, ...)
- It leave messages in internal cirtual buffer which has a fixed size
- If the buffer is full, the remaining messages will overwrite oldest messages until send out all the messages - Not reliable to deliver messages to user
rc = fc_remote_port_chkready(rport);
if (rc) {
printk(KERN_ERR PFX "els 0x%x: rport not ready\n", op);
rc = -EINVAL;
goto els_err;
}
- Kernel log level can be specified in the head of format string
- It’s defined in ‘include/linux/kernel.h’
#define KERN_EMERG "<0>" /* system is unusable */
#define KERN_ALERT "<1>" /* action must be taken immediately */
#define KERN_CRIT "<2>" /* critical conditions */
#define KERN_ERR "<3>" /* error conditions */
#define KERN_WARNING "<4>" /* warning conditions */
#define KERN_NOTICE "<5>" /* normal but significant condition */
#define KERN_INFO "<6>" /* informational */
#define KERN_DEBUG "<7>" /* debug-level messages */
- The log goes to internal log buffer in kernel
- It’s defined in compile time by the below configuration
config LOG_BUF_SHIFT
int "Kernel log buffer size (16 => 64KB, 17 => 128KB)"
range 12 21
default 17
help
Select kernel log buffer size as a power of 2.
Examples:
17 => 128 KB
16 => 64 KB
15 => 32 KB
14 => 16 KB
13 => 8 KB
12 => 4 KB
- In case of RHEL7, it’s defined as 20 (1MB)
$ grep LOG_BUF_SHIFT config-3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64
CONFIG_LOG_BUF_SHIFT=20
-
In RHEL6, it’s 19 (512KB)
-
If you want to make kernel to print all the logs on console (not terminal), you can use the below
echo 8 > /proc/sys/kernel/printk
Character Device Driver
Major/Minor Numbers
- Identifies which device driver needs to be called to operate application requests
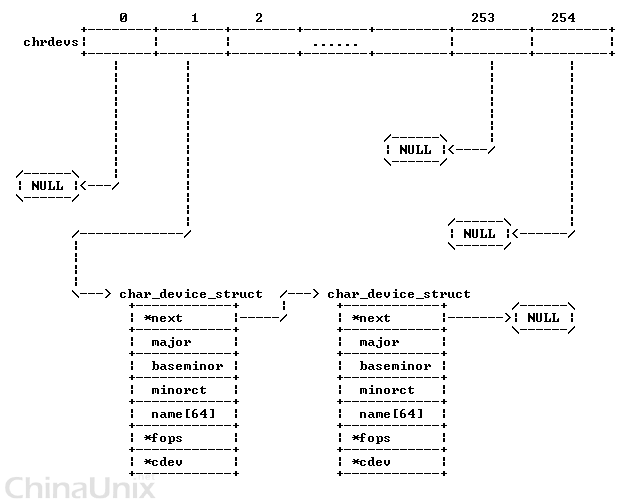
- Each file under /dev has major and minor number to identify which device driver with which function it needs to be called
root@devel:dev$ ls -l /dev/sd* /dev/tty?
brw-rw----. 1 root 8, 0 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/sda
brw-rw----. 1 root 8, 1 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/sda1
brw-rw----. 1 root 8, 2 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/sda2
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 0 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty0
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 1 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty1
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 2 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty2
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 3 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty3
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 4 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty4
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 5 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty5
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 6 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty6
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 7 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty7
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 8 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty8
crw--w----. 1 root 4, 9 Aug 13 11:23 /dev/tty9
- Currently registered device drivers can be found in /proc/devices
root@devel:dev$ egrep -e 'Character' -e 'Block' /proc/devices -A 5
Character devices:
1 mem
4 /dev/vc/0
4 tty
4 ttyS
5 /dev/tty
--
Block devices:
2 fd
259 blkext
8 sd
9 md
11 sr
- The files under /dev/ with major/minor are called ‘device node’
- A device node can be created with ‘mknod’ command or system call. Deleting a node is same as normal file deleting
mknod -m 666 /dev/myharddisk b 8 0
mknod /dev/myserial c 4 0
- Major/Minor number is handled in kernel with type ‘dev_t’.
typedef __u32 __kernel_dev_t;
typedef __kernel_dev_t dev_t;
- Major/Minor can be extracted or generated with the below macros
#define MAJOR(dev) ((dev)>>8)
#define MINOR(dev) ((dev) & 0xff)
#define MKDEV(ma,mi) ((ma)<<8 | (mi))
more precise macros are in the below
#define MINORBITS 20
#define MINORMASK ((1U << MINORBITS) - 1)
#define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS))
#define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK))
#define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi))
character device driver registration
- In 2.4 kernel, registering character device driver was super easy. There’s an array as you can see in below and registering is taking one entry with details
struct device_struct{
const char * name;
struct file_operations *fops;
};
static struct device_struct chrdevs[MAX_CHRDEV];
- Registering was handled with the below functions which stills exist for compatibility
static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,
const struct file_operations *fops);
static inline void unregister_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name);
- In 2.6 kernel, we need to have a struct defined in ‘include/linux/cdev.h’
struct cdev {
struct kobject kobj;
struct module *owner;
const struct file_operations *ops;
struct list_head list;
dev_t dev;
unsigned int count;
};
- To register it, firstly, we need to allocate/initialize/register major ‘cdev’ data structure.
/* allocate a cdev structure */
struct cdev *cdev_alloc(void);
/* initialize a cdev structure */
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev, const struct file_operations *fops);
/* Increase reference count for this module and for the cdev structure */
static struct kobject *cdev_get(struct cdev *p);
/* Decrease reference count from this module and from the cdev structure */
void cdev_put(struct cdev *p);
/* add a char device to the system */
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p, dev_t dev, unsigned count);
/* remove a cdev from the system */
void cdev_del(struct cdev *p);
- Reserve Major/Minor number area (region)
/* register a range of device numbers */
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name);
/* register a range of char device numbers. major will be choosen automatically */
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count,
const char *name);
/* unregister a range of @count device numbers, starting with @from. */
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count);
- Registration example)
if (major) {
dev_id = MKDEV(major, 0);
retval = register_chrdev_region(dev_id, CS5535_GPIO_COUNT,
NAME);
} else {
retval = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev_id, 0, CS5535_GPIO_COUNT,
NAME);
major = MAJOR(dev_id);
}
if (retval) {
release_region(gpio_base, CS5535_GPIO_SIZE);
return -1;
}
printk(KERN_DEBUG NAME ": base=%#x mask=%#lx major=%d\n",
gpio_base, mask, major);
cdev_init(&cs5535_gpio_cdev, &cs5535_gpio_fops);
cdev_add(&cs5535_gpio_cdev, dev_id, CS5535_GPIO_COUNT);
- Unregistration example)
static void __exit cs5535_gpio_cleanup(void)
{
dev_t dev_id = MKDEV(major, 0);
cdev_del(&cs5535_gpio_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev_id, CS5535_GPIO_COUNT);
release_region(gpio_base, CS5535_GPIO_SIZE);
}
- Actual operations need to be specified in ‘struct file_operations’
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);
int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t);
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
int (*ioctl) (struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*fsync) (struct file *, struct dentry *, int datasync);
int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync);
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **);
};
- Let’s make a simple character device driver with fixed major number (mychar.c)
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#define MYDEV_NAME "mycdrv"
#define KBUF_SIZE 10 * PAGE_SIZE
static char *kbuf;
static dev_t first;
static unsigned int count = 10;
static int my_major = 900, my_minor = 0;
static struct cdev *my_cdev;
static int my_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
printk(" OPEN device : %s\n", MYDEV_NAME);
return 0;
}
static int my_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
printk(" CLOSE device : %s\n", MYDEV_NAME);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t my_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf,
size_t lbuf, loff_t *ppos) {
int nbytes = lbuf - copy_to_user(buf, kbuf + *ppos, lbuf);
*ppos += nbytes;
printk("\n my_read, nbytes=%d, pos=%d\n", nbytes, (int)*ppos);
return nbytes;
}
static ssize_t my_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf,
size_t lbuf, loff_t *ppos) {
int nbytes = lbuf - copy_from_user(kbuf + *ppos, buf, lbuf);
*ppos += nbytes;
printk("\n my_write, nbytes=%d, pos=%d\n", nbytes, (int)*ppos);
return nbytes;
}
static loff_t my_lseek(struct file *file, loff_t offset, int orig) {
loff_t testpos;
switch (orig) {
case 0: testpos = offset; break;
case 1: testpos = file->f_pos + offset; break;
case 2: testpos = KBUF_SIZE + offset; break;
default: return -EINVAL;
}
testpos = testpos < KBUF_SIZE ? testpos : KBUF_SIZE;
testpos = testpos >= 0 ? testpos : 0;
file->f_pos = testpos;
return testpos;
}
static struct file_operations my_fops = {
.llseek = my_lseek,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = my_open,
.release = my_release,
.read = my_read,
.write = my_write,
};
static int __init my_init(void) {
kbuf = kmalloc(KBUF_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
first = MKDEV(my_major, my_minor);
register_chrdev_region(first, count, MYDEV_NAME);
my_cdev = cdev_alloc();
cdev_init(my_cdev, &my_fops);
cdev_add(my_cdev, first, count);
printk("Success\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit my_exit(void) {
cdev_del(my_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(first, count);
kfree(kbuf);
printk("\nunregistered\n");
}
module_init(my_init);
module_exit(my_exit);
- Makefile
$ cat Makefile
obj-m += mychar.o
export KROOT=/lib/modules/`uname -r`/build
allofit: modules
modules:
@$(MAKE) -C $(KROOT) M=$(PWD) modules
modules_install:
@$(MAKE) -C $(KROOT) M=$(PWD) modules_install
clean:
rm -rf *.o *.ko .*cmd *.mod.c .tmp_versions .*.d .*.tmp Module.symvers
- Test steps
$ insmod ./mychar.ko
$ lsmod | head -n 2
Module Size Used by
mychar 12710 0
$ grep mycdrv /proc/devices
900 mycdrv
$ mknod /dev/mydrv c 900 0
$ echo "Hello" > /dev/mydrv
$ head /dev/mydrv
Hello
��`J�������������������n�W udelay(1);
wait_time++;
} while (wait_time < REQSACK_TIMEOUT_TIME);
nsp32_msg(KERN_WARNING, "wait SACK timeout, ack_bit: 0x%x", ack_bit);
}
$ rmmod mychar
$ echo "Hello" > /dev/mydrv
-bash: /dev/mydrv: No such device or address
$ ls -l /dev/mydrv
crw-r--r--. 1 root 900, 0 Aug 18 15:54 /dev/mydrv
$ rm -rf /dev/mydrv
$
- Let’s use dynamic major number (mydynamic.c)
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#define MYDEV_NAME "mycdrv"
#define KBUF_SIZE (size_t)(10*PAGE_SIZE)
static char *kbuf;
static dev_t first;
static unsigned int count = 1;
static struct cdev *my_cdev;
static int mycdrv_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
static int counter = 0;
printk(" attempting to open device: %s:\n", MYDEV_NAME);
printk(" MAJOR number = %d, MINOR number = %d\n",
imajor(inode), iminor(inode));
counter++;
printk(" successfully open device: %s:\n\n", MYDEV_NAME);
printk("I have been opened %d times since being loaded\n", counter);
printk("ref=%ld\n", module_refcount(THIS_MODULE));
return 0;
}
static int mycdrv_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk(" CLOSING device: %s:\n\n", MYDEV_NAME);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t
mycdrv_read(struct file *file, char __user * buf, size_t lbuf, loff_t * ppos)
{
int nbytes, maxbytes, bytes_to_do;
maxbytes = KBUF_SIZE - *ppos;
bytes_to_do = maxbytes > lbuf ? lbuf : maxbytes;
if (bytes_to_do == 0)
printk("Reached end of the device on a read");
nbytes = bytes_to_do - copy_to_user(buf, kbuf + *ppos, bytes_to_do);
*ppos += nbytes;
printk("\n Leaving the READ function, nbytes=%d, pos=%d\n", nbytes,
(int)*ppos);
return nbytes;
}
static ssize_t
mycdrv_write(struct file *file, const char __user * buf, size_t lbuf,
loff_t * ppos)
{
int nbytes, maxbytes, bytes_to_do;
maxbytes = KBUF_SIZE - *ppos;
bytes_to_do = maxbytes > lbuf ? lbuf : maxbytes;
if (bytes_to_do == 0)
printk("Reached end of the device on a write");
nbytes = bytes_to_do - copy_from_user(kbuf + *ppos, buf, bytes_to_do);
*ppos += nbytes;
printk("\n Leaving the WRITE function, nbytes=%d, pos=%d\n", nbytes,
(int)*ppos);
return nbytes;
}
static loff_t mycdrv_lseek(struct file *file, loff_t offset, int orig)
{
loff_t testpos;
switch (orig) {
case 0: /* SEEK_SET */
testpos = offset;
break;
case 1: /* SEEK_CUR */
testpos = file->f_pos + offset;
break;
case 2: /* SEEK_END */
testpos = KBUF_SIZE + offset;
break;
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
testpos = testpos < KBUF_SIZE ? testpos : KBUF_SIZE;
testpos = testpos >= 0 ? testpos : 0;
file->f_pos = testpos;
printk("Seeking to pos=%ld\n", (long)testpos);
return testpos;
}
static const struct file_operations mycdrv_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = mycdrv_read,
.write = mycdrv_write,
.open = mycdrv_open,
.release = mycdrv_release,
.llseek = mycdrv_lseek
};
static int __init my_init(void)
{
if (alloc_chrdev_region(&first, 0, count, MYDEV_NAME) < 0) {
printk("failed to allocate character device region\n");
return -1;
}
if (!(my_cdev = cdev_alloc())) {
printk("cdev_alloc() failed\n");
unregister_chrdev_region(first, count);
return -1;
}
cdev_init(my_cdev, &mycdrv_fops);
kbuf = kmalloc(KBUF_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (cdev_add(my_cdev, first, count) < 0) {
printk("cdev_add() failed\n");
cdev_del(my_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(first, count);
kfree(kbuf);
return -1;
}
printk("\nSucceeded in registering character device %s\n", MYDEV_NAME);
printk("Major number = %d, Minor number = %d\n",
MAJOR(first), MINOR(first));
return 0;
}
static void __exit my_exit(void)
{
if (my_cdev)
cdev_del(my_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(first, count);
if (kbuf)
kfree(kbuf);
printk("\ndevice unregistered\n");
}
module_init(my_init);
module_exit(my_exit);
- Makefile
$ cat Makefile
obj-m += mychar.o mydynamic.o
export KROOT=/lib/modules/`uname -r`/build
allofit: modules
modules:
@$(MAKE) -C $(KROOT) M=$(PWD) modules
modules_install:
@$(MAKE) -C $(KROOT) M=$(PWD) modules_install
clean:
rm -rf *.o *.ko .*cmd *.mod.c .tmp_versions .*.d .*.tmp Module.symvers
- Test it
$ insmod mydynamic.ko
$ lsmod | head -n 2
Module Size Used by
mydynamic 12772 0
$ grep mycdrv /proc/devices
249 mycdrv
$ mknod /dev/mycdrv c 249 0
$ echo "Hello" > /dev/mycdrv
$ head /dev/mycdrv
Hello
��`J��������������������n�W udelay(1);
wait_time++;
} while (wait_time < REQSACK_TIMEOUT_TIME);
nsp32_msg(KERN_WARNING, "wait SACK timeout, ack_bit: 0x%x", ack_bit);
}
/*
$ rmmod mydynamic
$ rm -rf /dev/mycdrv
udev - device manager for Linux 2.6
- With udev (userspace device), we don’t need to create/delete a device node manually each time device is registered/unregistered
extern struct class * __must_check __class_create(struct module *owner,
const char *name,
struct lock_class_key *key);
extern void class_destroy(struct class *cls);
/* This is a #define to keep the compiler from merging different
* instances of the __key variable */
#define class_create(owner, name) \
({ \
static struct lock_class_key __key; \
__class_create(owner, name, &__key); \
})
struct device *device_create(struct class *class, struct device *parent,
dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...);
void device_destroy(struct class *class, dev_t devt);
- Let’s rewrite the code to make it create device nodes automatically
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/version.h>
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE < KERNEL_VERSION(2,6,13)
#define class class_simple
#define class_create class_simple_create
#define device_create class_simple_device_add
#define device_destroy(class,first) \
class_simple_device_remove(first)
#define class_destroy class_simple_destroy
#endif
struct class *my_class;
#define MYDEV_NAME "mydrv"
#define KBUF_SIZE (int)(10 * PAGE_SIZE)
static char *kbuf;
static dev_t first;
static unsigned int count = 5;
static struct cdev *my_cdev;
int my_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
static int counter = 0;
printk(" my_open(%s)\n\n", MYDEV_NAME);
printk(" major = %d, minor = %d\n",
imajor(inode), iminor(inode));
counter++;
printk("counter = %d\n", counter);
return 0;
}
int my_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
printk(" my_release(%s)\n", MYDEV_NAME);
return 0;
}
ssize_t my_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf,
size_t lbuf, loff_t *ppos) {
int nbytes, maxbytes, bytes_to_do;
maxbytes = KBUF_SIZE - *ppos;
bytes_to_do = maxbytes > lbuf ? lbuf : maxbytes;
if (bytes_to_do == 0) {
printk("reach end of the device\n");
return -ENOSPC;
}
nbytes = bytes_to_do - copy_to_user(buf, kbuf + *ppos,
bytes_to_do);
*ppos += nbytes;
printk("\n my_read, nbytes = %d, pos = %d\n",
nbytes, (int)*ppos);
return nbytes;
}
char to_lower(char c) {
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') return c - 'A' + 'a';
return c;
}
char to_upper(char c) {
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') return c - 'a' + 'A';
return c;
}
int convert(char *kbuf_str, size_t lbuf, int minor) {
int i;
char c;
for (i = 0; i < lbuf; i++) {
c = *(kbuf_str + i);
switch (minor) {
case 1: c = to_lower(c); break;
case 2: c = to_upper(c); break;
}
*(kbuf_str + i) = c;
}
return lbuf;
}
ssize_t my_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf,
size_t lbuf, loff_t *ppos) {
struct inode *inode = file->f_dentry->d_inode;
int minor = MINOR(inode->i_rdev);
int nbytes, maxbytes, bytes_to_do;
maxbytes = KBUF_SIZE - *ppos;
bytes_to_do = maxbytes > lbuf ? lbuf : maxbytes;
if (bytes_to_do == 0) {
printk("Reach end of the device\n");
return -ENOSPC;
}
nbytes = bytes_to_do - copy_from_user(kbuf + *ppos,
buf, bytes_to_do);
convert(kbuf + *ppos, nbytes, minor);
*ppos += nbytes;
printk("\n my_write : nbytes = %d, pos = %d\n",
nbytes, (int)*ppos);
return nbytes;
}
struct file_operations my_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = my_read,
.write = my_write,
.open = my_open,
.release = my_release,
};
int __init my_init(void) {
int i;
dev_t node_no;
if (alloc_chrdev_region(&first, 0, count, MYDEV_NAME)<0) {
printk("Failed to allocate character device\n");
return -1;
}
if (!(my_cdev = cdev_alloc())) {
printk("cdev_alloc() failed\n");
unregister_chrdev_region(first, count);
return -1;
}
cdev_init(my_cdev, &my_fops);
kbuf = kmalloc(KBUF_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (cdev_add(my_cdev, first, count) < 0) {
printk("cdev_add() failed\n");
unregister_chrdev_region(first, count);
return -1;
}
my_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "mydrv");
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
node_no = MKDEV(MAJOR(first), i);
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE < KERNEL_VERSION(2,6,13)
device_create(my_class, node_no, NULL,
"mydrv%d", i);
#else
device_create(my_class, NULL, node_no,
NULL, "mydrv%d", i);
#endif
}
return 0;
}
void __exit my_exit(void) {
int i;
dev_t node_no;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
node_no = MKDEV(MAJOR(first), i);
device_destroy(my_class, node_no);
}
class_destroy(my_class);
if (my_cdev)
cdev_del(my_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(first, count);
if (kbuf) kfree(kbuf);
}
module_init(my_init);
module_exit(my_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- Test result
root@devel:kernel$ insmod ./mydynamic_udev.ko
root@devel:kernel$ lsmod | head -n 2
Module Size Used by
mydynamic_udev 12882 0
root@devel:kernel$ ls -l /dev/mydrv*
crw-------. 1 root 249, 0 Sep 28 16:47 /dev/mydrv0
crw-------. 1 root 249, 1 Sep 28 16:47 /dev/mydrv1
crw-------. 1 root 249, 2 Sep 28 16:47 /dev/mydrv2
crw-------. 1 root 249, 3 Sep 28 16:47 /dev/mydrv3
crw-------. 1 root 249, 4 Sep 28 16:47 /dev/mydrv4
root@devel:kernel$ grep mydrv /proc/devices
249 mydrv
root@devel:kernel$ rmmod mydynamic_udev
root@devel:kernel$ ls -l /dev/mydrv*
ls: cannot access /dev/mydrv*: No such file or directory
root@devel:kernel$ grep mydrv /proc/devices
root@devel:kernel$
Module reference counter
- If you want to protect your module from unloaded when it’s doing operations, you need to increase module reference counter
- ‘rmmod’ only unloads when reference counter is 0.
bool try_module_get(struct module *module);
void module_put(struct module *module);
unsigned long module_refcount(struct module *mod);
- example
try_module_get(THIS_MODULE);
printk("Ref count=%ld\n", module_refcount(THIS_MODULE));
module_put(THIS_MODULE);