I/O handling via port
Two types of hardware access
- Memory mapped control (example: video memory)
- I/O port control (Serial, Parallel, etc)
Functions for I/O port access
- Basic functions
/* Basic port I/O */
static inline void outb(u8 v, u16 port)
{
asm volatile("outb %0,%1" : : "a" (v), "dN" (port));
}
static inline u8 inb(u16 port)
{
u8 v;
asm volatile("inb %1,%0" : "=a" (v) : "dN" (port));
return v;
}
static inline void outw(u16 v, u16 port);
static inline u16 inw(u16 port);
static inline void outl(u32 v, u16 port);
static inline u32 inl(u16 port);
static inline void io_delay(void)
{
const u16 DELAY_PORT = 0x80;
asm volatile("outb %%al,%0" : : "dN" (DELAY_PORT));
}
- Functions reading more than one data
static inline void insb(unsigned long addr, void *buffer, int count);
static inline void insw(unsigned long addr, void *buffer, int count);
static inline void insl(unsigned long addr, void *buffer, int count);
static inline void outsb(unsigned long addr, const void *buffer, int count);
static inline void outsw(unsigned long addr, const void *buffer, int count);
static inline void outsl(unsigned long addr, const void *buffer, int count);
Reserve port range
- To notify to others that this port range is already taken, it’s recommended to allocate port range before the operation with the one of the below functions
/* Convenience shorthand with allocation */
#define request_region(start,n,name) __request_region(&ioport_resource, (start), (n), (name), 0)
#define request_muxed_region(start,n,name) __request_region(&ioport_resource, (start), (n), (name), IORESOURCE_MUXED)
#define __request_mem_region(start,n,name, excl) __request_region(&iomem_resource, (start), (n), (name), excl)
#define request_mem_region(start,n,name) __request_region(&iomem_resource, (start), (n), (name), 0)
#define request_mem_region_exclusive(start,n,name) \
__request_region(&iomem_resource, (start), (n), (name), IORESOURCE_EXCLUSIVE)
#define rename_region(region, newname) do { (region)->name = (newname); } while (0)
- Once all operations finished on
#define release_region(start,n) __release_region(&ioport_resource, (start), (n)) #define check_mem_region(start,n) __check_region(&iomem_resource, (start), (n)) #define release_mem_region(start,n) __release_region(&iomem_resource, (start), (n)) - Currently occupied port ranges
$ head /proc/ioports
0000-0cf7 : PCI Bus 0000:00
0000-001f : dma1
0020-0021 : pic1
0040-0043 : timer0
0050-0053 : timer1
0060-0060 : keyboard
0064-0064 : keyboard
0070-0071 : rtc0
0080-008f : dma page reg
00a0-00a1 : pic2
Example: Control built-in speaker
- Needs to control two part
- Speaker : Port 0x61
- Frequency : Port 0x40, 0x41, 0x42, 0x43
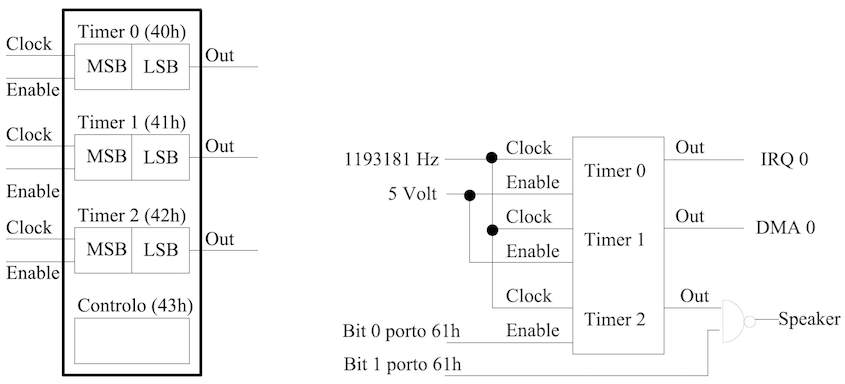
- Control speaker
- Enable: set bit 0 and bit 1 on port 0x61
- Disable: unset bit 0 and bit 1 on port 0x61
- Frequency control
- Intel PIT (8253/8254 chip)
- 0x40 (Channel 0) : System clock update
- 0x41 (Channel 1) : DMA control refresh
- 0x42 (Channel 2) : Frequency
- 0x43 (Control port) : Select port
- 0x43 port’s bits consists of the below
- Bit 7, 6: Channel selection
- Bit 5, 4: Data order
- Bit 3, 2, 1 : Mode
- Bit 0: Format (BCD or Binary)
- For the frequency, we are using 0xB6 (Set on bit 7, 5, 4, 2, 1)
- 0x42 sets the frequency calculated by the below
- 2 bytes <== 1193180 / frequency
- Code for the sound control
#define CLK_FREQ (1193180L)
#define PIO (0x61)
#define PIT_CMD (0x43)
#define PIT_DATA (0x42)
#define SETUP (0xB6)
#define TONE_ON (0x03)
#define TONE_OFF (0xFC)
void sound(int freq)
{
unsigned int value = inb(PIO);
freq = CLK_FREQ / freq;
if ((value & TONE_ON) == 0) {
outb(value | TONE_ON, PIO);
outb(SETUP, PIT_CMD);
}
outb(freq & 0xff, PIT_DATA);
}
outb(freq & 0xff, PIT_DATA);
outb((freq >> 8) & 0xff, PIT_DATA);
}
void nosound(void)
{
unsigned int value = inb(PIO);
value &= TONE_OFF;
outb(value, PIO);
}
- Let’s write a character device drivers that plays morse code
- We can express each character by following the table in the table
- Use character device as it’s easier to implement and to test
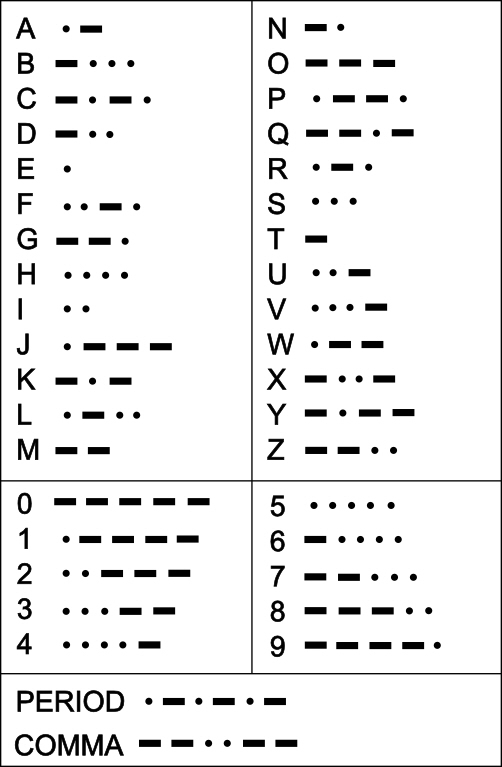
- Simplest version with many possible issues
/* morse_io.c */
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#define CLK_FREQ (1193180L)
#define PIO (0x61)
#define PIT_CMD (0x43)
#define PIT_DATA (0x42)
#define SETUP (0xB6)
#define TONE_ON (0x03)
#define TONE_OFF (0xFC)
void sound(int freq)
{
unsigned int value = inb(PIO);
freq = CLK_FREQ / freq;
if ((value & TONE_ON) == 0) {
outb(value | TONE_ON, PIO);
outb(SETUP, PIT_CMD);
}
outb(freq & 0xff, PIT_DATA);
outb((freq >> 8) & 0xff, PIT_DATA);
}
void nosound(void)
{
unsigned int value = inb(PIO);
value &= TONE_OFF;
outb(value, PIO);
}
#undef BIT_MASK
#define SPACE_MASK (1 << 15)
#define BIT_MASK (0xFE)
#define UNIT_TIME (60)
#define FREQUENCY (2000)
void send_dot(void)
{
sound(FREQUENCY);
mdelay(UNIT_TIME);
nosound();
mdelay(UNIT_TIME);
}
void send_dash(void)
{
sound(FREQUENCY);
mdelay(UNIT_TIME * 3);
nosound();
mdelay(UNIT_TIME);
}
void letter_space(void)
{
mdelay(UNIT_TIME * 2);
}
void word_space(void)
{
mdelay(UNIT_TIME * 4);
}
void morse(char *cp)
{
unsigned int c;
static unsigned int codes[64] = {
SPACE_MASK, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 115, 49, 106, 41,
63, 62, 60, 56, 48, 32, 33, 35,
39, 47, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 76,
0, 6, 17, 21, 9, 2, 20, 11,
16, 4, 30, 13, 18, 7, 5, 15,
22, 27, 10, 8, 3, 12, 24, 14,
25, 29, 19
};
while ((c = *cp++) != '\0') {
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z')
c = c - 'a' + 'A';
c -= ' ';
if (c > 58)
continue;
c = codes[c];
if (c & SPACE_MASK) {
word_space();
continue;
}
while (c & BIT_MASK) {
if (c & 1)
send_dash();
else
send_dot();
c >>= 1;
}
letter_space();
}
}
ssize_t m_write(struct file *filp, const char *buffer,
size_t length, loff_t * offset)
{
char *data = (char *)kmalloc(length, GFP_KERNEL);
if (data == NULL)
return 0;
length = length - copy_from_user(data, buffer, length);
data[length] = 0;
morse(data);
kfree(data);
return length;
}
struct file_operations m_fops = {
.write = m_write
};
int major_no = 0;
int init_module()
{
major_no = register_chrdev(0, "morse", &m_fops);
return 0;
}
void cleanup_module()
{
unregister_chrdev(major_no, "morse");
}
- Makefile
obj-m += morse_io.o
export KROOT=/lib/modules/`uname -r`/build
allofit: modules
modules:
@$(MAKE) -C $(KROOT) M=$(PWD) modules
modules_install:
@$(MAKE) -C $(KROOT) M=$(PWD) modules_install
clean:
rm -rf *.o *.ko .*cmd *.mod.c .tmp_versions .*.d .*.tmp Module.symvers modules.order
- Test run
$ make
make[1]: Entering directory `/usr/src/kernels/3.10.0-123.20.1.el7.x86_64'
CC [M] /root/kernel/morse_io.o
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST 7 modules
CC /root/kernel/morse_io.mod.o
LD [M] /root/kernel/morse_io.ko
make[1]: Leaving directory `/usr/src/kernels/3.10.0-123.20.1.el7.x86_64'
$ insmod ./morse_io.ko
$ grep morse /proc/devices
248 morse
$ mknod /dev/morse c 248 0
$ echo SOS > /dev/morse
$ rm /dev/morse
rm: remove character special file ‘/dev/morse’? y
$ rmmod morse_io
-
It contains many issues include manual device node creation
-
If you are trying the below, it’ll crash the system
$ sysctl -w kernel.softlockup_panic=1
$ cat morse_io.c > /dev/morse
- The problem is it’s staying in kernel until it’s play all the characters requested without any CPU yield
- To make delays, we are using ‘mdelay()’. There are some variations of this type of delay and the below are showing mdelay() and udelay()/ndelay().
- The problem with these functions is that it’s using looping which is consuming CPU power
/* 0x10c7 is 2**32 / 1000000 (rounded up) */
#define udelay(n) \
({ \
if (__builtin_constant_p(n)) { \
if ((n) / 20000 >= 1) \
__bad_udelay(); \
else \
__const_udelay((n) * 0x10c7ul); \
} else { \
__udelay(n); \
} \
})
/* 0x5 is 2**32 / 1000000000 (rounded up) */
#define ndelay(n) \
({ \
if (__builtin_constant_p(n)) { \
if ((n) / 20000 >= 1) \
__bad_ndelay(); \
else \
__const_udelay((n) * 5ul); \
} else { \
__ndelay(n); \
} \
})
void __udelay(unsigned long usecs)
{
__const_udelay(usecs * 0x000010c7); /* 2**32 / 1000000 (rounded up) */
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__udelay);
void __ndelay(unsigned long nsecs)
{
__const_udelay(nsecs * 0x00005); /* 2**32 / 1000000000 (rounded up) */
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__ndelay);
inline void __const_udelay(unsigned long xloops)
{
int d0;
xloops *= 4;
asm("mull %%edx"
:"=d" (xloops), "=&a" (d0)
:"1" (xloops), "0"
(this_cpu_read(cpu_info.loops_per_jiffy) * (HZ/4)));
__delay(++xloops);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__const_udelay);
#ifndef mdelay
#define mdelay(n) (\
(__builtin_constant_p(n) && (n)<=MAX_UDELAY_MS) ? udelay((n)*1000) : \
({unsigned long __ms=(n); while (__ms--) udelay(1000);}))
#endif
Side notes: How to check loop count)
calibrate_delay();
cpu_data(cpuid).loops_per_jiffy = loops_per_jiffy;
....
pr_info("Total of %d processors activated (%lu.%02lu BogoMIPS)\n",
num_online_cpus(),
bogosum/(500000/HZ),
(bogosum/(5000/HZ))%100);
- As it’s not yielding CPUs to other processes, that will cause of long delay and will be detected as a softlockup.
- To avoid this situation, it’s better to use the below functions instead
void msleep(unsigned int msecs);
unsigned long msleep_interruptible(unsigned int msecs);
-
It’ll go to sleep for that time frame, so other processes can take the CPU and the sysem won’t get blocked
- Also, the original device driver uses deprecated functons for registering/unregistering character device.
- Let’s reimplement it to have recent style functions and don’t cause of system hang
- Here, I’m using the internal implementation similar to msleep() in morse_mdelay().
/* morse_io.c */
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#define MORSE_CLK_FREQ (1193180L)
#define MORSE_PIO (0x61)
#define MORSE_PIT_CMD (0x43)
#define MORSE_PIT_DATA (0x42)
#define MORSE_SETUP (0xB6)
#define MORSE_TONE_ON (0x03)
#define MORSE_TONE_OFF (0xFC)
void sound(int freq)
{
unsigned int value = inb(MORSE_PIO);
freq = MORSE_CLK_FREQ / freq;
if ((value & MORSE_TONE_ON) == 0) {
outb(value | MORSE_TONE_ON, MORSE_PIO);
outb(MORSE_SETUP, MORSE_PIT_CMD);
}
outb(freq & 0xff, MORSE_PIT_DATA);
outb((freq >> 8) & 0xff, MORSE_PIT_DATA);
}
void nosound(void)
{
unsigned int value = inb(MORSE_PIO);
value &= MORSE_TONE_OFF;
outb(value, MORSE_PIO);
}
#define MORSE_SPACE_MASK (1 << 15)
#define MORSE_BIT_MASK (0xFE)
#define MORSE_UNIT_TIME (60)
#define MORSE_FREQUENCY (2000)
void morse_mdelay(int ms)
{
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
schedule_timeout((ms * HZ) / 1000);
}
void send_dot(int minor_no)
{
sound(MORSE_FREQUENCY * minor_no);
morse_mdelay(MORSE_UNIT_TIME);
nosound();
morse_mdelay(MORSE_UNIT_TIME);
}
void send_dash(int minor_no)
{
sound(MORSE_FREQUENCY * minor_no);
morse_mdelay(MORSE_UNIT_TIME * 3);
nosound();
morse_mdelay(MORSE_UNIT_TIME);
}
void letter_space(int minor_no)
{
morse_mdelay(MORSE_UNIT_TIME * 2);
}
void word_space(int minor_no)
{
morse_mdelay(MORSE_UNIT_TIME * 4);
}
void morse(char *cp, int minor_no)
{
unsigned int c;
static unsigned int codes[64] = {
MORSE_SPACE_MASK, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 115, 49, 106, 41,
63, 62, 60, 56, 48, 32, 33, 35,
39, 47, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 76,
0, 6, 17, 21, 9, 2, 20, 11,
16, 4, 30, 13, 18, 7, 5, 15,
22, 27, 10, 8, 3, 12, 24, 14,
25, 29, 19
};
while ((c = *cp++) != '\0') {
if (c < 'A')
continue;
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z')
c = c - 'a' + 'A';
c -= ' ';
if (c > 58)
continue;
c = codes[c];
if (c & MORSE_SPACE_MASK) {
word_space(minor_no);
continue;
}
while (c & MORSE_BIT_MASK) {
if (c & 1)
send_dash(minor_no);
else
send_dot(minor_no);
c >>= 1;
}
letter_space(minor_no);
}
}
ssize_t m_write(struct file *filp, const char *buffer,
size_t length, loff_t * offset)
{
struct inode *inode = filp->f_dentry->d_inode;
int minor_no = MINOR(inode->i_rdev) + 1;
char *data = (char *)kmalloc(length, GFP_KERNEL);
if (data == NULL)
return 0;
length = length - copy_from_user(data, buffer, length);
data[length] = 0;
morse(data, minor_no);
kfree(data);
return length;
}
struct file_operations m_fops = {
.write = m_write
};
int major_no = 0;
module_param(major_no, int, 0);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(major_no, "major number");
int minor_count = 3;
struct cdev *morse_cdev;
dev_t dev_id;
#define DEV_NAME "morse"
struct class *morse_class;
static int __init morse_init(void)
{
int retval;
int i;
if (major_no) {
dev_id = MKDEV(major_no, 0);
retval = register_chrdev_region(dev_id, minor_count, DEV_NAME);
} else {
retval = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev_id, 0, minor_count, DEV_NAME);
major_no = MAJOR(dev_id);
}
if (retval) {
return -1;
}
morse_cdev = cdev_alloc();
if (!morse_cdev) {
unregister_chrdev_region(dev_id, minor_count);
return -1;
}
cdev_init(morse_cdev, &m_fops);
cdev_add(morse_cdev, dev_id, minor_count);
morse_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, DEV_NAME);
for (i = 0; i < minor_count; i++) {
dev_t node_no = MKDEV(MAJOR(dev_id), i);
device_create(morse_class, NULL, node_no, NULL, DEV_NAME "%d",
i);
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit morse_exit(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < minor_count; i++) {
dev_t node_no = MKDEV(MAJOR(dev_id), i);
device_destroy(morse_class, node_no);
}
class_destroy(morse_class);
cdev_del(morse_cdev);
kfree(morse_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev_id, minor_count);
}
module_init(morse_init);
module_exit(morse_exit);
- Test run would be simpler than before
$ make
$ insmod ./morse_io.ko
$ echo SOS > /dev/morse0
$ echo SOS > /dev/morse1
$ echo SOS
$ rmmod morse_io